Exploring Kansei and Implicit Knowledge
Well being in an Information Society
In the future, commitment to a human-centered society based on enhanced collaboration with information technology, especially internet technology, is an important requirement for a better life. Our expectations are much higher than before. Therefore, expectations for high level artificial intelligence for computers are becoming much stronger than before. It is said that without exception, all people have “Kansei” and “Implicit knowledge”. One theory holds that “Implicit knowledge” is actually sharing more than 95% of all human knowledge. We humans are using these skills adeptly, adapting to various environments. Our laboratory is mainly focusing on these human’s “Kansei” and “Implicit knowledge” of daily life, from the broad points of view. Researching “Kansei” or “Implicit knowledge” requires flexible ingenuity and various methodologies. We also approach these 2 issues in diverse ways from various aspects. Perhaps it may sound exaggerating a little, but exploring what the origin of human “mind” is, how to treat or calculate it by computer, and how to collaborate such computers and humans, is a main theme of Matsui Laboratory.
Questions and Approaches
Interdisciplinary questions over human intelligence, human sense, human learning and human education are our research motivations.
- What is human sense? Is it possible to measure it?
- How do humans acquire knowledge? How to persuade them to do so? What persuades us to do so?
- Is it possible to represent skills and implicit knowledge? How to convey it?
- How to understand human behavior? Is it possible to predict it?
For these questions, we are trying to find answers through 2 approaches:
(1) analytically investigate situations and mechanisms,
(2) create integrated machines which support our research technically.
Utilizing statistic algorithms and artificial intelligence technologies is also one of Matsui Lab’s features, making us a leader in the field.
Research of Kansei media
“Kansei” is such a difficult theme to define. In the first place, it is a difficult research subject. However, it is also quite an interesting theme related to “personality” and “humanness”. What music gives us pleasure? Why are games interesting? Why do we feel that a sunset is beautiful?...and so forth.
To answer such questions, our research uses academic approaches based on preceding findings of cognitive science and psychology, underlying statistical knowledge and artificial intelligence technologies.
Construction of mathematical rules of color harmony
It is fact that people unconsciously sense preference for color combinations, but the mechanism has not been sufficiently detected yet. In this study, based on mathematical models and experimental approaches, we attempt to verify what kinds of color combinations are harmonious.

Image generaged by the experiment
Study of media representation of visual and auditory senses
Concerning communication media, it is to be expected that haptic media giving impressions through computers will become popular as daily tools in our everyday life. For effective media communication from the view points of cognition and affection, previous studies show that we cannot say it is always best to use visual media. In this research, we are aiming to find appropriate haptic information quantity, such as how much photographic reality is needed or what kinds of information should be given to images, and to express whole elements of what people want to convey. Using a haptic device “PHANTOM Omni”, we have been constructing mixed media of visual and haptic senses and been investigating impressions of it.
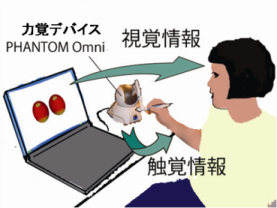
Experiment of evaluation of impression with haptic device
Study of the effects of impression of combining melodies and chord-progression
The impressions gained when listening to melodies are considered as a result of the combination of various factors such as rhythm, melody, harmony, tone and so forth. Some previous work had focused on each factor individually, and there seems to be no apparent study with respect to the interinfluence of each element. In this study, we have empirically experimented to verify our hypothesis that combing melodies and chord-progression would make unexpected effects for listeners’ impressions.
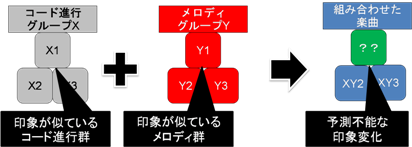
Impression change model of combining melodies and chord-progression
Empirical study of generating mechanisms of uncanny valley
There is a case when human replicas look and act almost, but not perfectly, like actual human beings, it causes a response of revulsion among human observers. This kind of phenomenon is known to happen not only for robot but also for computer graphic agents, and such agents can be looked at either as “human” or “agent” so that it can be considered people would evaluate them from both view points. In this work, we assume that some kind of gap between these evaluations would induce discomfort, and we study how impressions change based on only 2 pieces of information: “human” and “agent”.
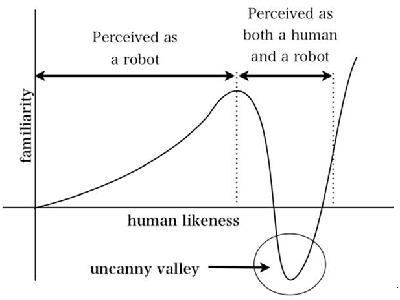
Relation of similarity between robot for human and human for robot(partially altered from that in [Mori, 1970])
Semantic Structure Analysis for onomatopoeia and Sensory Modalities in Communication of Visual Images
When we place an order with an advertising designer, an architect designer or costume designer, it is necesaary for us to share with him/her the ideal image of what we want. In our reaserch, in order to clarify the semantic structure of onomatopoeia, we try to interpret onomatopoeia on the basis of its degree of relevance to the five modalities (namely the visual sense, the auditory sense, the olfactory sense, the gustatory sense and the tactual sense) as well as its Order Relevance. One feature of onomatopoeia, which makes it special in the Japanese language, is that it can express directly the inner impression derived from five sensory modalities. We have extracted the Order Relevance of onomatopoeia words – for example, Assari, Nikkori, Ukiuki, e.t.c. – used in our experiment from their degrees of relevance to the five sensory modalities via Semantic Structure Analysis. And we aim to discover the rules of semantic interpretation of onomatopoeia that changes depending on the context and the usage.

Concept of Communication Model of Visual Images
Skills and Implicit Knowledge
People acquire various skills and knowledge and utilize them for daily life. However, it is quite difficult to know definitely what kind if skills and knowledge people have and how people acquired them. In fact, there exists so-called “Formal knowledge” that people can state the explicitly (for example, explain it in words for others), but is only a small part of their whole knowledge. It is said that almost all information is “Implicit knowledge” that is , difficult to express by words. This is one of the reasons to develop thinking machines “Artificial Intelligence”.
The breathing of physical action of classic ballet
This research is investigation the corresponding relationship between common choreographies of classic ballet. As the result of monitoring a dancer’s breathing during a performance, we found that there are particular ways of breathing during common ballet movements. Comparing ideal ballet breathing and that which was monitored, we found unconscious breathing without the teacher’s direction. Therefore, it can be considered that breathing is an important role to control ballet movement and body condition.
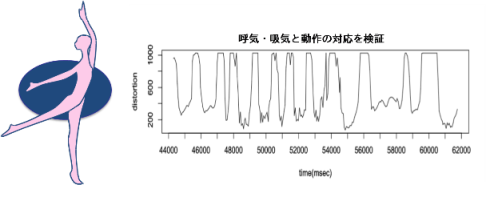
Coloration of breathing and body movement
Extracting method of expressing feeling of Japanese calligraphy
This is research to describe how a calligrapher conveys his/her feeling to a viewer. An expert calligrapher wrote 3 Japanese Kanji characters (with the meaning of dream, way, and wind) with 5 different feelings (normal, pleasure, angry, sad, enjoyment) (totally 15 pieces). Regarding these 15 characters, we extracted a method to express feeling underlying feature elements of each character. After categorizing them by one writing method called Eiji-Happou, we analyzed the way of expressing feeling by each writing method.
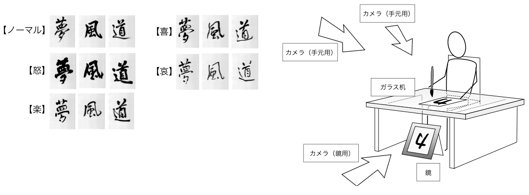
experiment environment
Formalization of "Pause" Expressing Transliteration Intention
This is a research on "Pause" during the reading of a written text by Transliteration Person. A Transliteration Person is someone who reads a written text for visually-impaired people. In order to faithfully convey the intention of the authors of the written texts, it is necessary for the Transliteration Person to read the texts with an accurate "Pause." So we have conducted an experiment aiming to clarify how to use "Pause." As a result, it was shown that "Short Pause" is important to the production of a reading faithful to a text. "Short Pause" is a Pause, the duration of which is 0.5 second or less. In future work, we are going to show that "Short Pause" is closely related to comfortable rhythm and tempo for a reading faithful to the written text.
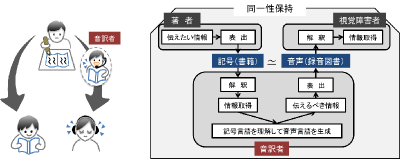
Transliteration Model on producing faithful talking book from original printed book
Intelligent Interface
Mainly, we attempt to support online education via computers and networks. This theme has a strong relationship between knowledge acquired, implicit knowledge and human sense, and their findings are to be a foundation of design concept of support systems. Adapting some technology of artificial intelligence, such as deducible technology and machine learning, we realize a system with an intelligent interface which can respond properly to a learner’s behavior.
Scientific study and engineered realization for idea generation support based on example cases
It is said that in many cases, people tend to utilize examples (past experiences or existent cases in society) to solve a problem or generate diverse ideas. Utilizing examples means that it is possible to use methods or successful solution for the past but it also means that it makes us conceive only similar ideas. In this research, we constructed a learner’s idea generation support system based on the findings of scientific study. In the case learners facing some types of creative task, what kind of example limits his/her ideas or makes them spread much wider, and how to make learners utilize examples to induce idea generation support. The experiment material is a mathematical example.
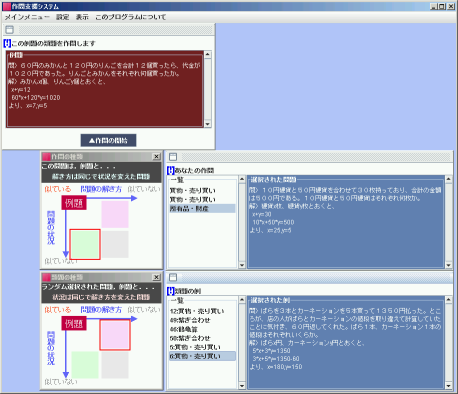
Screen shot of support system
Conjecture of mental state from human’s behavior
This research is aiming to conjecture mental state from human’s unintentional gestures. Almost all preceding work employed specialized extensive equipment un order to measure eye movement, electroencephalographic activity and so forth. However, in this study, we used only common tools such as a computer mouse or web camera without extensive machines, which is a distinct point from other work. We are going to this technology for developing systems to detect the level of concentration or wondering when people face choice questions projected on a computer screen to answer.
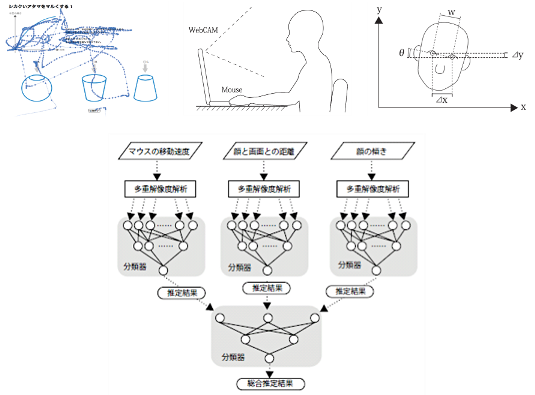
Model of conjecture of mental state based on neural network
Calculation models of intelligence and biology
Establish knowledge description and computational simulation models for prediction of biological phenomenon
Following are the main features and problems involved:
- Even if some findings infer the same meaning, it is difficult to share or reuse that knowledge since technical terms are not standardized.
- Due to the dispersion of individual variability, stored data tends to be qualitative. Therefore, it is not so easy to make computers understand or calculate that there are limitations to make simulations based on quantitative approaches.
Therefore in this research, we are utilizing artificial intelligence technology in order to solve these problems, for processing to construct simulation models of the prediction of biological phenomenon. To be more precise, focusing on one biological phenomena which is called apotosis (programmed cell suicide), constructing ontology-based architectonics in natural language over related knowledge (cellular location, movement, role) to translate information into a unifying description form that a computer can understand. Based on this knowledge description, we attempt to build a computer simulation model. Ontology is an algorithm, explicitly unified organizing information that makes it possible to let a computer understand information. It can be considered that with this approach it will be possible to find the existence of yet-to-be-defined systems and molecules.
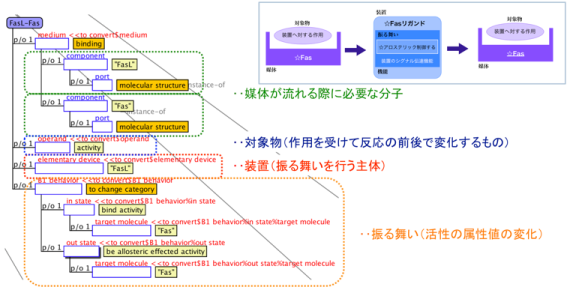
Ontology-based description of apotosis(one of the part)
Construct color emotion ontology and human computer interaction on a profound level
Humans can sense colors as “bright” ”warming” “beautiful” and share their affection with others. These affective reactions are called color emotion. Many multidisciplinary findings exist in wide fields over psychology, biology, engineering and so forth.
In this research, we are aiming to provide
(1) broad understanding of multidisciplinary findings of color attributes and emotional states,
(2) construct ontology of obtained findings of color emotion for providing necessary information for human-computer interaction.
It can be said that it is possible to share concept among researchers based on acquired findings, and this will make computers possible to become human-level understanding. Especially, it is expected that an interaction system developed on conceptual base will be able to share concepts on a profound level such as affect between humans and computers.

Human-Computer Interaction Model on the basis of the Ontology